 Although numerous methods exist for coupling two components, choosing the best option for the intended application requires an understanding of all available technologies. For example, when clamping a hub onto a shaft or axle, splined or keyway-based couplings are a popular choice. Another traditional method of connecting gears to shafts involves shrink fitting, which uses temperature differences between mated parts to create an interference fit that holds the parts together. Welding is another option, although it is a more permanent solution than a coupling device.
Although numerous methods exist for coupling two components, choosing the best option for the intended application requires an understanding of all available technologies. For example, when clamping a hub onto a shaft or axle, splined or keyway-based couplings are a popular choice. Another traditional method of connecting gears to shafts involves shrink fitting, which uses temperature differences between mated parts to create an interference fit that holds the parts together. Welding is another option, although it is a more permanent solution than a coupling device.
Yet another approach is to use locking assemblies, which offer several advantages over other coupling choices in terms of cost, reliability, contamination resistance, and ease of both installation and removal. Understanding the simple design, main features, and benefits of locking assemblies will help you determine whether or not they will work in your next coupling application.
HOW LOCKING ASSEMBLIES OPERATE
Locking assemblies are installed internally between the shaft and the hub. They feature a variety of designs consisting of either two, three, or four rings and have inner and outer rings; top, bottom, and outer rings; or inner, outer, rear, and front rings.
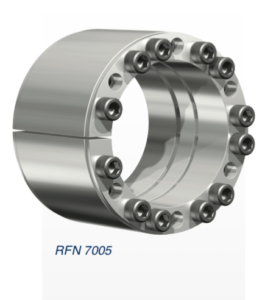 Tightening the locking screws with a torque wrench brings the rings together, compressing the inner ring onto the shaft while pushing the outer ring out into the hub. This applies pressure to the inside of the hub and secures it to the shaft using a friction-fit press connection. The resulting fit can handle extremely high forces, making it a great choice for light and heavy-duty applications alike.
Tightening the locking screws with a torque wrench brings the rings together, compressing the inner ring onto the shaft while pushing the outer ring out into the hub. This applies pressure to the inside of the hub and secures it to the shaft using a friction-fit press connection. The resulting fit can handle extremely high forces, making it a great choice for light and heavy-duty applications alike.
Due to an even distribution of compression forces around the shaft circumference, locking assembly couplings inherently prevent misalignment and offer maximum reliability with a strong and secure connection. Ringfeder’s locking assemblies use standard socket-head screws and tighten with standard tools. No additional machining or fitting is required. When it comes time for removal, disassembly is simple. After loosening the locking screws, the assembly self-releases, and the hub and shaft can move freely for adjustment, removal, or replacement as required. Depending on the type of locking assembly, you may need to use jacking screws to separate the rings.
DESIGN FEATURES AND BENEFITS
To understand the advantages of locking assemblies, it is helpful to compare them to other methods of coupling two parts. For example, when using traditional splined or keyed shafts, parts must be perfectly aligned. Not only does this approach carry the additional expense of machining the mating parts, it also creates a weak point or stress concentration factor. All of the load is carried on the key, making it the weakest point in the connection. This is not so with locking assemblies, which are much more forgiving in terms of alignment and do not require the same level of precision during installation.
Due to an even distribution of compression forces around the shaft and inside the hub circumferences, locking assembly couplings inherently prevent misalignment and offer maximum reliability with a strong and secure connection. Because the load is evenly dispersed around the shaft and within the hub, a locking assembly can handle more load for the same size shaft compared to a keyed or splined coupling. Stresses on the shaft are therefore much lower because they are evenly distributed by the locking assembly. Some of the most important benefits of this elegant coupling design include:
 Ease of use. Simplified installation and operation are notable advantages of locking assemblies. For example, in heavy-duty applications in which couplings can weigh as much as two tons, attempting to align and engage keyways during installation can be a difficult, frustrating and dangerous task. With locking assemblies, no stops, steps, keyways or splines are required; hubs can be located and locked into position at any point on the shaft. This means maximum positioning adjustability and much simpler and faster installation compared to keyways and splines.
Ease of use. Simplified installation and operation are notable advantages of locking assemblies. For example, in heavy-duty applications in which couplings can weigh as much as two tons, attempting to align and engage keyways during installation can be a difficult, frustrating and dangerous task. With locking assemblies, no stops, steps, keyways or splines are required; hubs can be located and locked into position at any point on the shaft. This means maximum positioning adjustability and much simpler and faster installation compared to keyways and splines.
With Ringfeder’s standard locking assembly series, high transmission values are possible: By varying the screw tightening torque, the assembly can easily be adapted to the design specification. Simplified manufacturing is another hallmark of working with Ringfeder locking assemblies. Only plain shaft and bore diameters with easily achievable surface finishes and tolerances are required. The entire system is more economical compared to using parts that involve extensive machining to achieve the same level of reliability and torque transmission.
Fast installation. The locking assembly mounting process is very straightforward. Ringfeder’s locking assemblies use standard screws and
tighten with standard tools, requiring no additional machining or fitting. Screws are tightened in a star/cross pattern, in quarter-turn increments until the recommended torque is achieved. Installation is therefore much easier than using keyways or splines that must be lined up perfectly, or in shrink-fit approaches where heating and/or cooling equipment fits parts together by creating a temperature differential.
Using such equipment adds more cost to the joining process and creates safety concerns with the risk of burns and other injuries. Locking assemblies require only a standard torque wrench for installation rather than a torch. In other words, a reliable interference fit is created by squeezing rather than heating.
Simple disassembly. When it is time to remove the coupling, disassembly is as simple as it gets. After loosening the locking screws evenly around the shaft with a standard wrench, the locking assembly self-releases, or jacking screws are used depending on design. The hub can then move freely on the shaft for removal or replacement as needed. This process is in stark contrast to shrink fit couplings, which often require several hours of heating with specialized equipment to pry the mated components apart. Additional workers are also typically required for both installation and removal of shrink fit couplings, especially when large sizes are involved.
Long service life. Reusability is another benefit to consider. Once the locking assemblies are removed, they may be reused several times. A simple inspection to check for damage is all that is required. Typically, the only part that may need replacing is an occasional screw. All screws should be inspected for wear, and if any are stretched or otherwise damaged, they should be replaced — a very economical alternative compared to purchasing a new coupling.
Superior materials. Ringfeder’s locking assemblies are made of high-strength, highly ductile steel. Depending on the application details, different materials are available to achieve various levels of strength, corrosion resistance, and other specifications. The material’s surface finish is another factor to consider when choosing a coupling device because the coefficient of friction (COF) affects the holding power. Ringfeder’s locking assemblies feature an exceptionally smooth finish and a documented COF.
Capabilities. Locking assemblies self-center around the shaft as well as within the hub, distributing pressures evenly due to the tightening method used. They also feature excellent concentricity, keeping the hub and shaft rotating uniformly around the center axis. This allows the weight of the hub to be distributed equally and maintains shaft and hub balance while in use.
Contamination resistance. When the assembly’s locking screws are tightened, contact surfaces are pressed firmly together to prevent dirt and moisture ingress. In contrast, designs with sharp corners, such as splines and keyways, are much more susceptible to contamination.
TECHNICAL ASSISTANCE AVAILABLE
For assistance with engineering calculations or customized designs for specialized applications, such as those requiring hollow shafts, Ringfeder’s engineering team is available for advice and consultation. The team can also help determine if a locking assembly is the best option for your next coupling application.
Ringfeder
www.ringfeder.com
Leave a Reply